月份: 六月 2022
如何使用Xposed+JustTrustMe来突破SSL Pinning
Xposed 簡易安裝暨操作流程
IoT firmware reverse engineer
資安事件排查 & 威脅情資
Team T5 執行長提供的參考資料
防堵私自架設DHCP伺服器
| 作 者:邱顯智 精誠資訊 優勢多媒體學苑資深講師 技術分類:網路管理類 每次都來亂相信大部分從事網路管理工作的朋友都曾經遭遇私自架設的DHCP伺服器在網路上亂發IP的問題,這種狀況一旦出現,將會造成部分員工無法正常連線到公司網路,然而要揪出這些私自架設的DHCP伺服器往往要花費很多精神與力氣,無奈這年頭能夠拿來當成DHCP伺服器的設備實在太多,包含安裝Windows Server系列或Linux作業系統的電腦、IP分享器、甚至是XP或Windows 7開啟「網際網路連線共用」功能的電腦都可以在網路上提供IP租用的服務,所以這種惱人的夢靨總是每隔一段時間就會重演一次。會造成這種狀況的原因在於當DHCP用戶端開機時他們會在網路上發出【DHCPDiscover】的廣播封包,嘗試尋找網路上的DHCP伺服器租用IP,而網路上的DHCP伺服器們則會回應【DHCPOffer】的廣播封包嘗試提供IP租用的服務,若DHCP用戶端收到來自多台DHCP 伺服器的DHCPOffer訊息時,就會向第一台提供Offer的DHCP伺服器發出【DHCPRequest】封包要求租用IP,該DHCP伺服器就會回應【DHCPAck】封包以確認用戶端的IP租用行為。 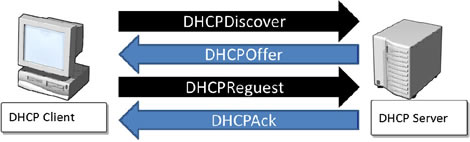 因此在下圖的網路中,網路上同時存在公司合法的DHCP伺服器(派發10.10.10.0/24網段的IP),以及非法私自架設的DHCP伺服器(派發192.168.0.0/24網段的IP),萬一網路上的用戶在租用IP的過程,私架的DHCP伺服器率先回應【DHCPOffer】的封包,因此用戶端租用到的IP會是192.168.0.0網段的IP,而不是公司正常規劃的10.10.10.0網段,而且這些用戶端也會跟著取得錯誤的Default Gateway、DNS Server…等選項資訊,自然他們就連不上公司正式網路了。 因此在下圖的網路中,網路上同時存在公司合法的DHCP伺服器(派發10.10.10.0/24網段的IP),以及非法私自架設的DHCP伺服器(派發192.168.0.0/24網段的IP),萬一網路上的用戶在租用IP的過程,私架的DHCP伺服器率先回應【DHCPOffer】的封包,因此用戶端租用到的IP會是192.168.0.0網段的IP,而不是公司正常規劃的10.10.10.0網段,而且這些用戶端也會跟著取得錯誤的Default Gateway、DNS Server…等選項資訊,自然他們就連不上公司正式網路了。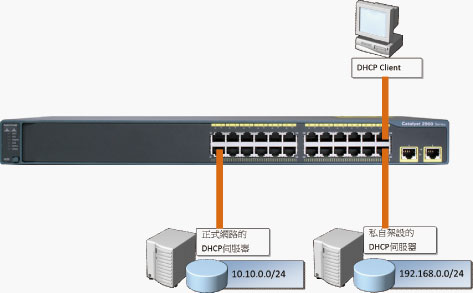 Cisco Switch上具備了【DHCP Snooping】功能可以防堵私自架設的DHCP伺服器在網路任意發放IP的問題,運作原理其實很簡單,也就是將此功能啟用之後(預設未啟用),所有的介面都會呈現【Untrust】狀態,只要是DHCP伺服器才會發送的【DHCPOffer】或【DHCPAck】這兩種訊息在Untrust介面上都會被攔阻下來,只允許透過Trust介面傳送,因此您可以先在CLI的Global Configuration Mode先透過【ip dhcp snooping】及【ip dhcp snooping vlan 10】指令把DHCP Snooping功能在業務部的VLAN 10啟用,再將連接通往合法DHCP伺服器的介面設定為【ip dhcp snooping trust】即可。如此一來,您就不用擔心網路上私自架設的DHCP伺服器干擾您業務部網路的正常運作了。指令範例: Cisco Switch上具備了【DHCP Snooping】功能可以防堵私自架設的DHCP伺服器在網路任意發放IP的問題,運作原理其實很簡單,也就是將此功能啟用之後(預設未啟用),所有的介面都會呈現【Untrust】狀態,只要是DHCP伺服器才會發送的【DHCPOffer】或【DHCPAck】這兩種訊息在Untrust介面上都會被攔阻下來,只允許透過Trust介面傳送,因此您可以先在CLI的Global Configuration Mode先透過【ip dhcp snooping】及【ip dhcp snooping vlan 10】指令把DHCP Snooping功能在業務部的VLAN 10啟用,再將連接通往合法DHCP伺服器的介面設定為【ip dhcp snooping trust】即可。如此一來,您就不用擔心網路上私自架設的DHCP伺服器干擾您業務部網路的正常運作了。指令範例:SW66# configure terminal SW66(config)# ip dhcp snooping SW66(config)# ip dhcp snooping vlan 1 SW66(config)# interface fastethernet 0/2 SW66(config-if)# ip dhcp snooping trust SW66(config-if)# end SW66# show ip dhcp snooping Switch DHCP snooping is enabled DHCP snooping is configured on following VLANs:1 Insertion of option 82 is enabledInterface Trusted Rate limit (pps)———————— ———- ——————-FastEthernet0/3 yes unlimite |
5g 接入網、承載網、核心網
O-RAN Fronthual C-U/Sync/Mgmt Planes and Protocol Stack

O-RAN Fronthual C-U/Sync/Mgmt Planes and Protocol Stack
Author6G, Open RAN, Tech Fundas, Telco Cloud, Wireless Testing
The interface between DU and RU is known as Fronthaul. When this interface allows to connect any vendor DU to any vendor RU, know as Open Fronthaul. To enable this multi vendor DU and RU interconnection some signaling formats and control messaging is required are detailed by Open Standard i.e. O-RAN Alliance as part of O-RAN fronthaul specification.
These specifications anticipated different scenarios about Distributed Unit (DU) and Radio Unit (RU) interaction, what the underlying 5G will demand, time synchronization issues between two endpoints, and it make it deployment ready for Service Providers. By addressing these issues, the O-RAN standard is ensuring inter-op between DU and RU vendors.

O-RAN Fronthaul defines following planes of operations:
- C-Plane (Control Plane): Control plane messages define the scheduling, coordination required for data transfer, beam-forming etc.
- Scheduling and beam-forming commands
- DL precoding configuration
- Mixed numerology and PRACH handling
- U-Plane (User Plane): User plane messages for efficient data transfer within the strict time limits of 5G numerologies.
- Support Data Compression
- I/Q data transfer
- DL data precoding
- S-Plane (Synchronization Plane) : Synchronization plane is responsible for the timing and sync aspects between the O-DU and O-RU. In Cloud RAN deployments, a high accurate synchronization is required between O-DU and O-RUs to achieve controlled linking for inter-O-RU sync operation for TDD, Carrier Aggregation using multiple O-RUs, MIMO, and similar processes. Using S-Plane, O-RAN fronthaul specifications support protocols such as PTP and SyncE to achieve high-accuracy synchronization on the O-RU side by synchronizing with the clock high-performance available at O-DU side.
- Synchronization Typologies
- PTP and SyncE profiles for Synchronization
- Time and Frequency Sync guidelines
- M-plane (Management Plane) : Management plane messages are used to manage the radio unit. M-Plane provides a variety of O-RU management functions to set parameters on the O-RU side as required by the C/U-Plane and S-Plane , e.g. manage O-RU software, perform fault management, etc. O-RAN fronthaul specification for M-Plane provides various parameters as data models to FCAPS functions. This data models eliminates dependence on each O-RU vendorʼs implementation and makes a real multi-vendor Open RAN possible
- Support Hierarchical/Hybrid Model
- C/U Plane IP and Delay management
- FCAPS including sync configuration and status
Protocol Stack for O-RAN Fronthaul
The O-RAN fronthaul specifications protocol stack of each above mentioned plane is shown in below picture.
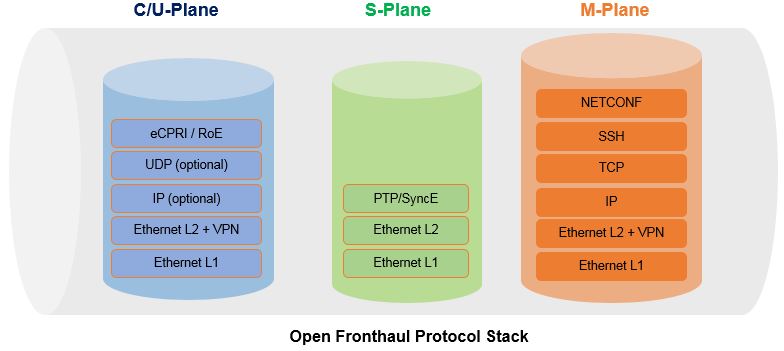
- C/U-Plane, the O-RAN fronthaul specifications support a protocol stack that transmits data used by eCPRI or Radio over Ethernet (RoE) directly over Ethernet and an optional protocol stack that transmits the signals over UDP/IP
- S-Plane in O-RAN fronthaul support a protocol stack that transmits data used in Precision Time Protocol (PTP) and SyncE over Ethernet
- M-Plane support a protocol stack that transmits signals used in NETCONF over Ethernet with IP transported using TCP with Secure SHell (SSH)






















